- Home
- About Us
-
Products
.png)
-
Application
.png)
-
Blog
.png)
- Contact us

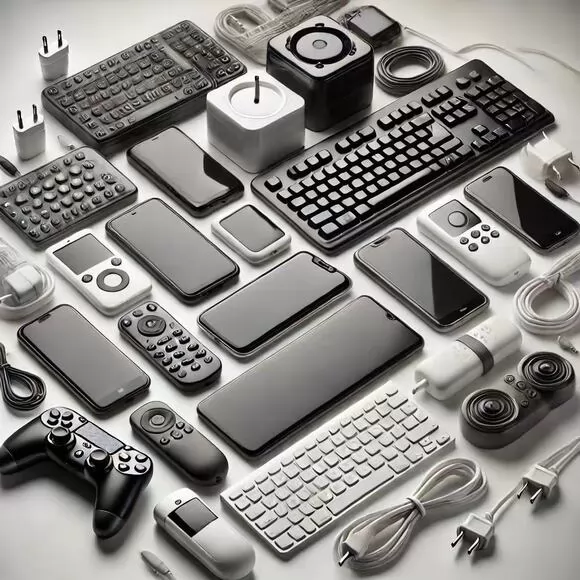
Electronic and Electrical Applications
KMT products are not only used in electrical cables, but also in circuit boards and housings for electronic devices. Their flame-retardant properties are especially valuable in components where overheating is a potential risk, such as power supplies, connectors, and insulation materials. The inclusion of Precipitated Magnesium Hydroxide and Aluminum Hydroxide enhances the flame resistance and overall performance of these products, ensuring safety and reliability in various applications.
Recommended grades include PM5SN, PM5S, and A1.


KMT all product series
| HP | Hexagonal Magnesium Hydroxide | HP7、HP7N |
| PM | Precipitated Magnesium Hydroxide | PM5SN、PM3SN、B3SN PM3E、PM3AS、PM3V PM5S、PM3S |
| HM | Hydromagnesite | HM2V、HM2SA、HM2E |
| B | Brucite Powder | B3.5、B3.5SA、B3.5S、B5、B10、B10ACP |
| A | Aluminum Hydroxide | A1 |
| APPLICATION | SUGGEST GRADE | ||||
| HP | PM | HM | B | A | |
| PE, POE, EPDM, EVA, XLPE, PVC, TPU, PA and ABS based compound. | HP7 HP7N | HM2SA | A1 | ||
| EVA/PE/POE low smoke halogen free cable compound | HP7 HP7N | PM5SN PM3SN B3SN | HM2SA | A1 | |
| PP compounds GF reinforced PP | PM5SN PM3SN | ||||
| FRLS PVC cable compounds LSFR PVC compounds | HP7 HP7N | PM3V | HM2V | A1 | |
| FR PE cable compounds | HP7 | PM3E | HM2E | A1 | |
| TPO and PVC roofing membranes | B3.5 B5 | ||||
| Aluminum composite panel | B10ACP | ||||
| Bedding compounds | B3SN | HM2SA | B10 | ||
| Others | Case by case For some special coating or mechanical requirement. | ||||
-
Wire and Cable
-
Building Materials
-
Electronic and Electrical Applications
-
Other Industrial Applications
Products
-
 Precipitated Magnesium HydroxideMgCl2+2NH3•H2O=Mg(OH)2↓+2NH4Cl Coated by KMT patent formula, easy dispersing in PP, PE, EVA, POE, EPDM, XLPE, PA, ABS compound.View All
Precipitated Magnesium HydroxideMgCl2+2NH3•H2O=Mg(OH)2↓+2NH4Cl Coated by KMT patent formula, easy dispersing in PP, PE, EVA, POE, EPDM, XLPE, PA, ABS compound.View All
-
 BruciteThe production of natural Brucite is started in the year 2008. We offer high purity and high whiteness Brucite powder. B series Brucite is widely used in PVC cable, HFFR cable compound, flame retardant panel, aluminum composite panel, flue gas desulfurization, wastewater treatment, magnesium fertilizer, etc.View All
BruciteThe production of natural Brucite is started in the year 2008. We offer high purity and high whiteness Brucite powder. B series Brucite is widely used in PVC cable, HFFR cable compound, flame retardant panel, aluminum composite panel, flue gas desulfurization, wastewater treatment, magnesium fertilizer, etc.View All
-
 Aluminum HydroxideHigh purity Aluminum Hydroxide can be used as halogen free flame retardant for plastic and rubber industry due to its well distributed granularity, good stability, non toxic and non-polluting.View All
Aluminum HydroxideHigh purity Aluminum Hydroxide can be used as halogen free flame retardant for plastic and rubber industry due to its well distributed granularity, good stability, non toxic and non-polluting.View All
FAQs

What are the differences between UL 94 V-0 and V-2 ratings?


UL 94 is a vertical burn test that rates the flame resistance of plastic materials on a scale of V-0 to V-5, with V-0 being the best. Here are the main differences between the V-0 and V-2 ratings:
• Burning time – For a V-0 rating, the flame must self-extinguish within 10 seconds of removing the ignition source. For V-2, it can take up to 30 seconds to self-extinguish. So V-0 indicates faster flame extinction.
• Dripping – For V-0, no dripping of flaming particles is allowed that continue burning. For V-2, a limited amount of flaming drips is allowed.
• flame spread – For V-0, flames cannot spread more than 100 mm (3.9 inches) along the sample. For V-2, flames can spread up to 150 mm (5.9 inches). So V-0 has lower flame spread.
• Number of specimens – V-0 requires that 5 specimens in a row pass the test, while V-2 only requires 2 consecutive specimens to pass. So V-0 represents more consistent performance.
In summary, the main differences come down to:
• Faster flame extinction time for V-0
• No flaming drips allowed for V-0
• Lower flame spread for V-0
• Higher consistency for V-0
The V-0 rating indicates significantly better flame resistance and higher fire safety performance. So flame retardant PVC formulations designed for applications with higher flame requirements will typically achieve a UL 94 V-0 rating rather than just V-2.
Hope this overview of the differences helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.

What are the most common applications for flame retardant PVC?


Here are some of the most common applications for flame retardant PVC:
• Electrical wire and cable insulation – PVC with a V-0 UL 94 rating is commonly used for wiring and cabling in buildings to help prevent the spread of fires.
• PVC plumbing pipes – Flame retardant PVC pipes are used for drainage, waste, and vent systems in buildings to meet fire safety codes.
• Construction materials – Flame retardant PVC is used for window frames, roofing membranes, flooring, and other building components where fire resistance is required.
• Medical devices and equipment – Flame retardant PVC tubing, sheets and coatings are used in products like oxygen masks, blood bags and medical appliances that must meet strict safety standards. Flame retardant PVC tubing, sheets and coatings are used in products like oxygen masks, blood bags and medical appliances
• Transportation components – Aviation grade flame retardant PVC is used for insulation, wire sheathing, hoses and other parts in vehicles, trains and aircraft to reduce fire risks.
• Industrial equipment – Flame retardant PVC components like cables, tubing, sheeting and coatings are used in machinery to help prevent the spread of fires.
• Furnishings and textiles – Flame retardant PVC coatings on upholstery fabrics, wall coverings and drapery meet fire safety requirements for use in public spaces.
As you can see, flame retardant PVC is critical for a wide range of applications where fire safety is essential. The flame resistant properties help prevent faster flame spread, reduce flammable droplets and achieve faster flame extinction – which are all vital for reducing fire risks and saving lives.
For example PVC cable compounds:
Here are some details about flame retardant PVC compounds for cable:
• Cable jacketing refers to the outer insulating layer of wire and cable assemblies. It protects and contains the inner conductors and insulation.
• Cable jacketing compounds are typically made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) resin compounded with various additives to achieve the required properties.compounds
• For electrical cables and wires, flame retardant PVC compounds are needed for the jacketing material to provide fire safety. These contain high amounts (30-40% by weight) of organohalogen flame retardants like decabromodiphenyl ether or chlorinated paraffin.
• Flame retardant PVC jacketing compounds are designed to achieve a UL 94 V-0 flame class rating or pass stringent vertical flame tests like IEC 60332-1, UL 1581 and UL 1685. This ensures the cables can self-extinguish quickly if ignited. Flame retardant PVC jacketing compounds are designed to achieve a UL 94 V-0 flame class rating or pass stringent vertical
• Other additives in flame retardant PVC jacketing compounds may include heat and UV stabilizers, lubricants, plasticizers and fillers to optimize properties like flexibility, aging resistance and hardness.
• Specialty flame retardant PVC jacketing compounds are available for high temperature, low smoke and halogen-free cables as well as for outdoor use and harsh environments. flame retardant PVC jacketing compounds are available for high temperature,
• Aviation grade and military specification flame retardant PVC compounds are used for jacketing aircraft wires and military application cables to meet very stringent flame test requirements.
• The flame retardant PVC jacketing helps prevent fire from spreading along cable runs and also reduces smoke and toxic gas emissions if combustion does occur. This improves safety for people and equipment.
Hope these details about flame retardant PVC cable jacketing compounds are helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

The key point for flame retardant PVC


The key requirement for flame retardant PVC is to achieve self-extinguishing properties. This means that if the PVC is exposed to a flame or ignition source, it should quickly stop burning on its own once the flame is removed. This is critical to reduce the spread of fire and improve safety.
Flame retardant additives are used in PVC to help meet this requirement. They work by:
Releasing substances that coat the burning surface and interfere with combustion reactions. This can choke off the flame and oxygen supply.
Interrupting the carbon chain reaction that is responsible for the flame propagation in burning PVC. This can lead to faster flame extinction.
Forming a char layer that acts as a physical barrier and prevents heat and combustible gases from reaching the underlying PVC. This can help the flame from regaining its foothold.
All of these mechanisms help the flame retardant PVC to self-extinguish more quickly once the ignition source is removed. This is the behavior that is evaluated in flame tests like UL 94 and vertical flame tests. The faster self-extinguishing times and lower flame spread indicate better flame retardant performance.
To summarize, achieving self-extinguishing properties through the use of flame retardant additives is the key requirement for making PVC flame resistant. This is what improves the fire safety and performance of flame retardant PVC products for their intended applications.
Hope this explanation of the key requirement for flame retardant PVC is helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.
Here are some additional details about flame retardant PVC:
Types of flame retardants used:
• Brominated flame retardants are most common, like decabromodiphenyl ether and tetrabromobisphenol A. They work by releasing bromine radicals that interrupt combustion reactions.
• Chlorinated flame retardants like chlorinated paraffin are also used. They release chloride ions that can coat burning surfaces.
• Inorganic flame retardants like aluminum trihydroxide, magnesium hydroxide and antimony trioxide can form an inert protective char layer.
• Phosphorus-based flame retardants like triaryl phosphate esters interrupt the combustion reactions by binding with radicals.
Issues with halogenated flame retardants:
• They can release corrosive and toxic halogen acid gases when burned.
• Many are persistent organic pollutants that bioaccumulate and remain in the environment for a long time.
• Some brominated flame retardants have been restricted due to health concerns.
Alternative flame retardants:
• Nanoparticle filled PVC that forms a protective barrier when heated.
• PVC formulations with higher chlorine content to provide some inherent flame resistance.
• Surface treatments that leave a intumescent coating on the PVC.
• Combinations of halogen-free flame retardants to improve efficiency.
• Flame retardant plasticizers that enhance the flame resistance of the PVC compound.
Faster self-extinguishing leads to better fire safety since it:
• Reduces flame spread potential
• Shortens the duration of combustion
• Lowers smoke and toxic gas emissions
So improving the self-extinguishing properties of PVC through appropriate flame retardant additives and formulations is the most important factor in making flame retardant PVC products safer.
Hope this additional information is helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

What are some alternative flame retardants that can be used in PVC products?


Here are some alternative flame retardants that can be used in PVC products:
• Aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)3) – It forms an inert alumina layer upon heating that acts as a physical barrier and flame retardant. It is a mineral flame retardant with relatively low toxicity.
• Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) – Similar to aluminum hydroxide, it forms a protective shield of magnesia when exposed to heat that inhibits flame spread. It is also a non-halogen flame retardant.
• KMT Industrial B2V is Mg based product, after test, B2V has an amazing performance in PVC products, it’s perfect!
Compared with other flame retardants, B2V can increase the oxygen index of PVC polymer (3-5%), and has more advantages in comprehensive cost. The comprehensive cost mentioned here refers to the cost per ton of PVC polymer.
• Phosphorus-based – Flame retardants like ammonium polyphosphate and resorcinol bis(diphenyl phosphate) that interrupt combustion by releasing phosphoric acid and releasing radicals. They are more environmentally sustainable options.
• Zinc borate – Acts as a flame retardant by releasing pyrolysis products that dilute combustible gases and releasing boric acid to coat burning surfaces. It is a halogen-free alternative.
• Nanoclay/nanosilica – Inorganic nanoparticles added to PVC that form a char layer upon heating. This barrier limits the transfer of heat and combustible products.
• Intumescent coatings – Systems that foam up and expand when exposed to heat, creating a thick layer of insulation that isolates the flame. Can be applied to the surface of PVC products.
• Combinations – Blends of multiple halogen-free flame retardants, like aluminum hydroxide with phosphorus compounds, are often used to achieve synergistic effects with lower additive levels.
These alternative non-halogen flame retardants provide more sustainable and eco-friendly options for flame retardant PVC products. While they tend to be less efficient on a per unit weight basis, combinations and synergistic effects can help improve their performance.
Research is ongoing to develop even more effective alternative flame retardants for PVC that do not have the health and environmental concerns associated with halogenated options.
Hope this overview of alternative flame retardants for PVC is useful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

How do flame tests like UL 94 evaluate the flame retardant performance of PVC?


Flame tests like UL 94 evaluate the flame retardant performance of PVC based on several key criteria:
Burning time – The time it takes for the PVC sample to self-extinguish after removing the ignition source is measured. Faster self-extinguishing indicates better flame retardant performance.
Flame spread – The distance that the flame travels along the PVC sample is measured. Lower flame spread shows the material is resisting flame propagation better.
Dripping – The amount and persistence of flaming droplets from the burning PVC is observed. Less dripping of flaming particles is considered better performance.
Smoke emission – Some flame tests measure the amount of smoke emitted from the burning PVC sample. Less smoke production can indicate better flame retardancy.
Char length – The remaining length of charred material after the test is measured. Shorter char lengths suggest a faster extinction of flame within the material.
Condition of ignited area – The test evaluators observe the condition of the area directly exposed to the flame. Less damage and deformation is considered better performance.
Repeatability – Some flame tests require that multiple PVC samples pass the test in a row. This shows the flame retardant properties are consistent and repeatable.
In the UL 94 vertical burn test specifically, PVC materials are rated on a V-0 to V-5 scale based primarily on burning time, flame spread and dripping behavior. The lower the rating (V-0 being the best), the better flame retardant performance.
So in summary, flame tests evaluate a combination of factors related to how quickly and completely the flame retardant PVC self-extinguishes, how much it resists flame spread, and what byproducts are released when burned. All of these criteria provide an indication of the material’s overall fire safety and flame resistance.
Hope this overview of how flame tests evaluate PVC is useful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

What are some common applications of flame-retardant PVC products?


Here are some common applications of flame retardant PVC products:
• Electrical wire and cable insulation – Flame retardant PVC is often used as insulation for household, industrial and building wiring to help prevent the spread of electrical fires. Flame retardant PVC is often used as insulation for household, industrial and building wiring to help prevent the
• PVC plumbing and drainage pipes – Flame retardant PVC pipes are used for residential and commercial plumbing and drainage systems to meet code requirements and improve fire safety.
• Roofing membranes and sheets – Flame retardant PVC roofing materials are used in commercial, industrial and institutional buildings to help reduce the risk of fire spread.
• Furnishings and textiles – Flame retardant PVC coated fabrics are used for upholstery, drapery, wall coverings and other applications to meet flammability standards for public spaces.
• Medical devices and equipment – Medical grade flame retardant PVC tubing, sheets and coatings are used in equipment like oxygen masks, ventilators and surgical instruments to meet strict safety requirements.
• Automotive and transportation components – Flame retardant PVC insulation, wire sheathing and hoses are used in vehicles, aircraft and mass transit systems to reduce fire risks and improve passenger safety.
• Industrial machinery components – Flame retardant PVC parts like cables, gaskets, tubes and sheets are used in production machinery, appliances and electronics to improve fire safety.
As you can see, flame retardant PVC products are critical for a wide range of common applications where fire resistance is needed for safety, code compliance or performance requirements. The flame retardant properties help prevent faster flame spread, reduce flammable droplets and achieve faster flame extinction.
Hope this overview of common flame retardant PVC applications is helpful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

Does the truck PVC tarpaulin need to be flame retardant?


Truck tarpaulins made from flame retardant PVC are recommended for safety reasons. Here are some reasons why flame retardant PVC tarpaulins are a good choice for truck covers:
Safety – Flame retardant properties help reduce fire risks associated with things like static electricity discharges, engine exhausts, and road debris impacts. This improves safety for drivers and people near the truck.
Code compliance – Some jurisdictions require that tarpaulins used on commercial trucks have flame retardant properties in order to comply with fire safety regulations. Flame retardant PVC can help meet these codes. flame retardant properties in order to comply with fire safety
UV resistance – Flame retardant formulations for PVC tarpaulins often include UV inhibitors and stabilizers to improve resistance to sunlight damage. This helps maintain the flame retardant properties over the life of the cover.
Heat resistance – The flame retardant additives and other chemical systems in flame retardant PVC can improve its thermal stability and resistance to high temperatures. This is useful for truck covers exposed to engine heat.
Durability – Properly formulated flame retardant PVC tarpaulin compounds contain additional additives that maintain the mechanical properties needed for durability and long lifespan as a truck cover.
Self-extinguishing – The key requirement of flame retardant PVC is that it achieves a self-extinguishing property. This means any flame that starts is quickly put out, reducing fire risks and spread.
So in summary, flame retardant PVC tarpaulins are recommended for truck covers due to the improved safety, code compliance, durability, UV and heat resistance they can provide. The flame retardant properties help reduce the risk of fires starting and spreading.
Hope this explanation helps! Let me know if you have any other questions.

Using flame retardant PVC tarpaulins advantage and disadvantage?


Here are the main advantages of flame retardant PVC tarpaulins:
Safety – The flame retardant properties help reduce the risk of fire and improve safety. This is critical for truck covers.
Code compliance – Flame retardant PVC tarpaulins can help meet fire safety regulations for commercial vehicle covers in some jurisdictions.
UV resistance – The flame retardant formulations often include UV stabilizers to maintain the properties when exposed to sunlight. This extends the lifespan of the cover.
Heat resistance – The additives improve the thermal stability of the PVC, making it more suitable for withstanding the heat from truck engines.
Self-extinguishing – The key functionality of flame retardant PVC is that it achieves a self-extinguishing property. Any flames that do start will quickly go out, reducing fire risks.
Durability – With the proper balance of additives, flame retardant PVC compounds for tarpaulins can provide durability comparable to standard PVC.
Aesthetics – High quality flame retardant PVC tarpaulins can still provide an opaque and colorful cover while achieving the required flame retardant properties. flame retardant PVC tarpaulins can still provide an opaque and colorful cover.
Cost effectiveness – Though initially more expensive, the reduced risk of fire damage and extended lifespan can make flame retardant PVC tarpaulins a cost effective choice in the long run.
In summary, the main advantages focus on improving the safety, durability and performance of PVC truck tarpaulins through the use of special flame retardant compounds. While there are some potential downsides as well, the benefits related to fire safety and risk reduction are the most compelling advantages for choosing flame retardant PVC.
Hope this overview of the key pros is useful! Let me know if you have any other questions about flame retardant PVC tarpaulins.
There are some potential downsides to using flame retardant PVC tarpaulins:
Toxic byproducts – Some of the flame retardant additives used in flame retardant PVC, especially halogenated compounds, can release toxic and corrosive gases if combusted. This could pose a risk to people near the truck in a fire.
Environmental impact – Some flame retardant chemicals used in PVC, like brominated compounds, can persist and accumulate in the environment. This can potentially cause ecological impacts if the tarpaulin ends up as litter or waste.
Higher cost – Flame retardant PVC compounds typically cost more than standard PVC due to the added flame retardant additives and special manufacturing requirements. This increases the cost of the tarpaulin.
Reduced flexibility – The flame retardant additives can sometimes make the PVC stiffer and less flexible. This could potentially impact the ease of installation and usage of the tarpaulin on the truck.
Shorter lifespan – Some flame retardant formulations may be more prone to UV and heat degradation over time, resulting in a potentially shorter lifespan for the tarpaulin before replacement is needed.
Difficulty recycling – Flame retardant PVC products can be more challenging to recycle due to issues with separating the flame retardant additives. This could reduce the recyclability of the tarpaulin at end of life.
So in summary, while flame retardant PVC tarpaulins provide benefits in terms of safety and flame retardant PVC tarpaulins provide benefits in terms of safety andcode compliance, there are also some potential issues related to toxic byproducts, environmental impact, cost, performance and recyclability. Manufacturers aim to minimize these downsides through formulation optimization while still achieving the required flame retardant properties.
Hope this overview of both pros and cons is useful! Let me know if you have any other questions.

-

 +86-931-7653361
+86-931-7653361 Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China.
Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China. -
Quick Links
-
Products