- Home
- About Us
-
Products
.png)
-
Application
.png)
-
Blog
.png)
- Contact us

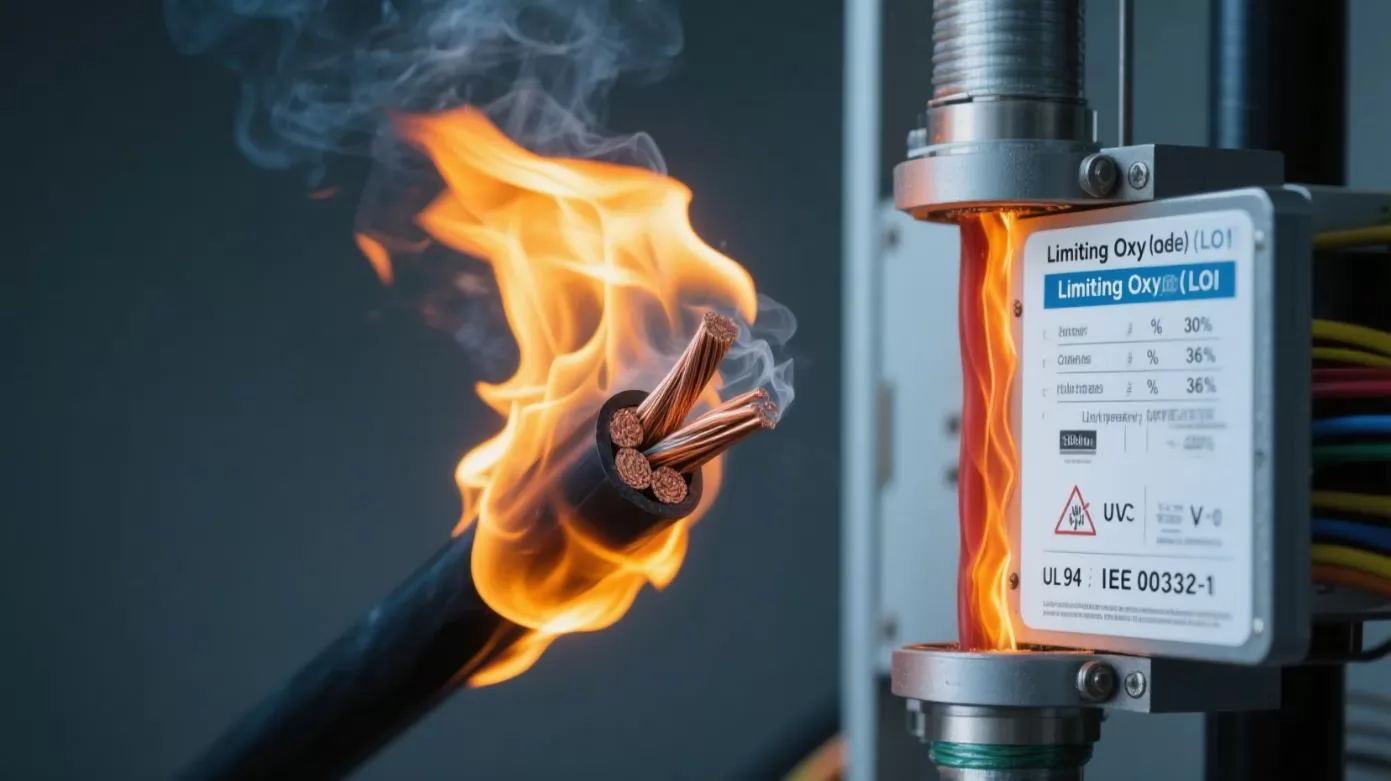
Optimizing Flame Retardant Performance in PVC Cable Compounds

Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cable compounds are essential for electrical applications, requiring outstanding flame retardant performance, alongside robust physical, mechanical, and electrical properties. Achieving this balance is critical for ensuring safety and compliance with industry standards like UL 94 and IEC 60332. This article explores the factors influencing flame retardant performance, measured by the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI), and provides actionable insights for optimizing PVC formulations.
Understanding Flame Retardant Performance
The flame retardant performance of PVC cable compounds is evaluated using the Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI), which measures the minimum oxygen concentration needed to sustain combustion. A higher LOI indicates better resistance to fire. Typically, an LOI above 30 signifies strong flame retardancy, while compounds with an LOI exceeding 36 are considered high-performance, ideal for demanding applications like power cables and building wiring.
Beyond LOI, compliance with standards such as UL 94 V-0 (vertical burning test) and IEC 60332-1 (single cable flame test) ensures that PVC compounds meet global safety requirements. These standards assess flame spread, smoke production, and self-extinguishing properties, all critical for flame retardant performance.

Key Factors Influencing Flame Retardant Performance
1. Impact of Plasticizer Content
Plasticizers enhance the flexibility of PVC cable compounds but significantly affect flame retardant performance. Common plasticizers include dioctyl terephthalate (DOTP), trioctyl trimellitate (TOTM), and tricresyl phosphate. Their impact includes:
- Oxygen Index Reduction: Higher plasticizer content lowers the LOI, reducing flame retardancy. For example, increasing DOTP from 20% to 40% can decrease LOI by 5-10 points, depending on the formulation.
- Smoke Generation: Elevated plasticizer levels increase smoke production during combustion, posing safety risks in confined spaces like data centers.
- Smoke Suppression: Phosphate-based plasticizers (e.g., tricresyl phosphate) and TOTM improve smoke suppression, enhancing safety in fire scenarios.
To optimize formulations, manufacturers should select plasticizers with inherent flame-retardant properties and limit their dosage to maintain an LOI above 30.
2. Role of Flame Retardants
Inorganic flame retardants are critical for boosting flame retardant performance. Antimony trioxide (Sb₂O₃) is widely used, but its effectiveness depends on dosage and synergy with other additives:
- Sb₂O₃ Effects: Increasing Sb₂O₃ content raises the LOI linearly up to a point. For instance, adding 5-10 phr (parts per hundred resin) of Sb₂O₃ can increase LOI by 3-5 points.
- Limitations: Beyond a certain threshold (e.g., 15 phr), Sb₂O₃’s impact on LOI diminishes, requiring complementary flame retardants.
- Compound Systems: Combining Sb₂O₃ with zinc borate (ZB) and magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) creates a synergistic effect, significantly boosting LOI. For example, a Sb₂O₃/ZB/Mg(OH)₂ blend can achieve an LOI above 36, ideal for high-flame-retardant cables.
Emerging eco-friendly flame retardants, such as aluminum hydroxide (ATH), are gaining traction due to their low toxicity and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directives, further enhancing flame retardant performance sustainably.
3. Balancing Flame Retardancy with Other Properties
While high flame retardant performance is essential, excessive plasticizer or flame retardant content can compromise mechanical and electrical properties:
- Moderate Flame Retardancy (LOI < 34): At lower LOI levels, tensile strength, elongation, and dielectric properties remain largely unaffected, making these compounds suitable for general-purpose cables.
- High Flame Retardancy (LOI > 36): Significant reductions in mechanical properties (e.g., 20-30% loss in tensile strength) and electrical insulation occur, challenging applications like high-voltage insulation.
For example, a PVC compound with an LOI of 38 may exhibit reduced flexibility, impacting cable installation in tight spaces. Manufacturers must balance flame retardancy with performance to meet standards like ASTM D638 (tensile testing) and IEC 60227 (electrical properties).

Environmental and Safety Considerations
Modern PVC cable compounds must address environmental concerns alongside flame retardant performance. Traditional flame retardants like Sb₂O₃ are effective but face scrutiny due to toxicity concerns. Eco-friendly alternatives, such as ATH and Mg(OH)₂, release water vapor during combustion, reducing smoke and toxic gas emissions. These align with regulations like REACH and RoHS, ensuring safer and more sustainable products.
Additionally, low-smoke, zero-halogen (LSZH) PVC formulations are increasingly adopted in public infrastructure (e.g., subways, hospitals) to minimize smoke and corrosive gas emissions during fires, complementing high flame retardant performance.
Best Practices for Optimizing PVC Cable Compounds

To achieve superior flame retardant performance while maintaining overall quality, manufacturers should adopt the following practices:
- Precise Formulation: Control plasticizer and flame retardant ratios during kneading and granulation to optimize LOI and minimize smoke.
- Synergistic Flame Retardants: Use combinations like Sb₂O₃/ZB/Mg(OH)₂ or eco-friendly ATH for enhanced flame retardancy.
- Rigorous Testing: Conduct LOI tests (ASTM D2863), mechanical tests (ASTM D638), and electrical tests (IEC 60227) to ensure compliance with UL, IEC, and regional standards.
- Process Control: Maintain consistent production conditions, from raw material selection to extrusion, to ensure uniform flame retardant performance.
- Sustainability Focus: Incorporate eco-friendly additives to meet environmental regulations and customer demands for greener products.
Conclusion
Achieving exceptional flame retardant performance in PVC cable compounds requires a strategic approach to formulation, testing, and production. By balancing plasticizers, flame retardants, and eco-friendly additives, manufacturers can produce safe, high-performance cables that meet stringent safety and environmental standards. Ongoing research and innovation will continue to drive advancements in flame retardant performance, ensuring PVC compounds remain a cornerstone of electrical applications.
This article references Hu Ling’s study, “Comprehensive Performance of Flame-Retardant PVC Cable Compounds.” For further details or inquiries, contact our team at [insert contact information].
If any content infringes on intellectual property rights, please contact us to address the issue promptly.
Your Name*
Your Email*
-
2025-Aug-26PM5S Magnesium Hydroxide: The High-Performance, Cost-Effective Flame Retardant FillerPM5S: A cost-effective silane-coated magnesium hydroxide (MDH) flame retardant with advantages over brucite, ATH, and premium MDH—offering smoke suppression, char formation, and synergy with ATH.
-
2025-Jul-09AM3V: The Next-Generation Flame Retardant Replacing ATO in PVC CompoundsDiscover AM3V, KMT Industrial’s innovative flame retardant replacing ATO in PVC compounds. Achieve high LOI (≥30), low smoke density, and 1/15th the cost.
-
2025-Apr-23Optimizing Flame Retardant Performance in PVC Cable CompoundsMaster flame retardant performance in PVC cable compounds with expert insights on LOI, plasticizers, and eco-friendly additives. Optimize safety and compliance.

-

 +86-931-7653361
+86-931-7653361 Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China.
Room 1212, 1213, Jinhe Building, No. 1264 Beibinhe West Road, Anning District, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China. -
Quick Links
-
Products